UK Smart Grid Solutions for Future Energy
Smart grid solutions are intelligent upgrades to our traditional electrical grid, turning it into a responsive, two-way communication network. They use digital technology to manage efficiently the growing demands of electric vehicle (EV) charging and renewable energy integration.
Understanding the Smart Grid Revolution
Think of the UK's current electrical grid as a network of one-way streets. Power flows from large power stations straight to homes and businesses with very little conversation happening in between. This setup has served us well for a century but it is now struggling to keep up with modern demands like rapid EV charging and the unpredictable energy from wind turbines and solar panels.
A smart grid completely transforms this old model into a dynamic superhighway. It’s a bit like upgrading from an old landline telephone—which could only make and receive calls—to a modern smartphone. The smartphone doesn't just handle calls; it manages data, runs apps and communicates in countless ways. In much the same way, smart grid solutions enable a constant, two-way dialogue between energy suppliers and consumers.
This digital conversation allows the grid to do some amazing things:
- Respond instantly to sudden changes in energy demand and supply.
- Integrate distributed energy resources , like rooftop solar panels and local batteries.
- Manage complex loads , such as a cluster of rapid EV chargers, without causing blackouts.
- Automate fault detection , isolating problems to prevent widespread power cuts.
The Core Components of an Intelligent Grid
At the heart of this transformation are a few key technologies that give the grid its intelligence. Smart meters , for instance, act as the eyes and ears of the network. They provide real-time data on energy consumption, arming both consumers and grid operators with invaluable insights.
Meanwhile, automated controls and advanced software act as the brain, analysing all this data to make split-second decisions. This system can automatically balance the load—for example, by encouraging EV charging when there's a surplus of wind power or carefully managing demand from grid connections that are already under strain. You can learn more about how these elements create a cleaner and more connected world with ZPN's smart grids in our detailed guide.
By enabling this real-time communication and control, smart grid solutions ensure that our national infrastructure is not just more efficient but also more resilient and ready for a future powered by renewables and electric transport.
The Core Technologies of a Modern Smart Grid
A modern smart grid isn't just one single piece of kit. It’s built from several interconnected technologies that all work together to create an intelligent, responsive and efficient energy network. These are the building blocks that take our traditional grid and prepare it for the future—a future filled with complex demands like rapid EV charging and power flowing in from decentralised sources such as combined on-site renewables.
Think of the most basic level of these technologies as the grid's nervous system. They gather and transmit data in real time, giving the 'brain' of the system the information it needs to make smart decisions. This ensures power gets to where it’s needed, when it's needed, with as little waste as possible.
Advanced Metering and Grid Intelligence
The most visible piece of this puzzle for most people is the Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) , which includes the familiar smart meter in our homes and businesses. But it's far more than just a fancy billing device; a smart meter is a two-way communication tool. It provides a constant stream of data back to the grid operator about energy consumption patterns, voltage levels and power quality.
This level of detail allows for incredible precision in managing the grid. For consumers, it means accurate bills and the ability to see exactly how and when they use energy. For grid operators, this data is the foundation for everything from predicting demand spikes to spotting faults before they can cause widespread outages. It’s a data-first approach that’s critical for keeping the lights on.
This constant flow of information is what truly separates a smart grid from its old-fashioned predecessor. It allows the network to be proactive rather than reactive, anticipating challenges and optimising performance. Central to this are advanced technologies like AI automation for business , which help make intelligent decisions, run predictive analytics and manage energy across the entire network.
If you’d like to dig deeper, you can learn more about the role of AI and big data in revolutionising energy management in our detailed article.
The infographic below shows just how dynamic the relationship is between the central grid, suppliers, consumers and renewable energy sources.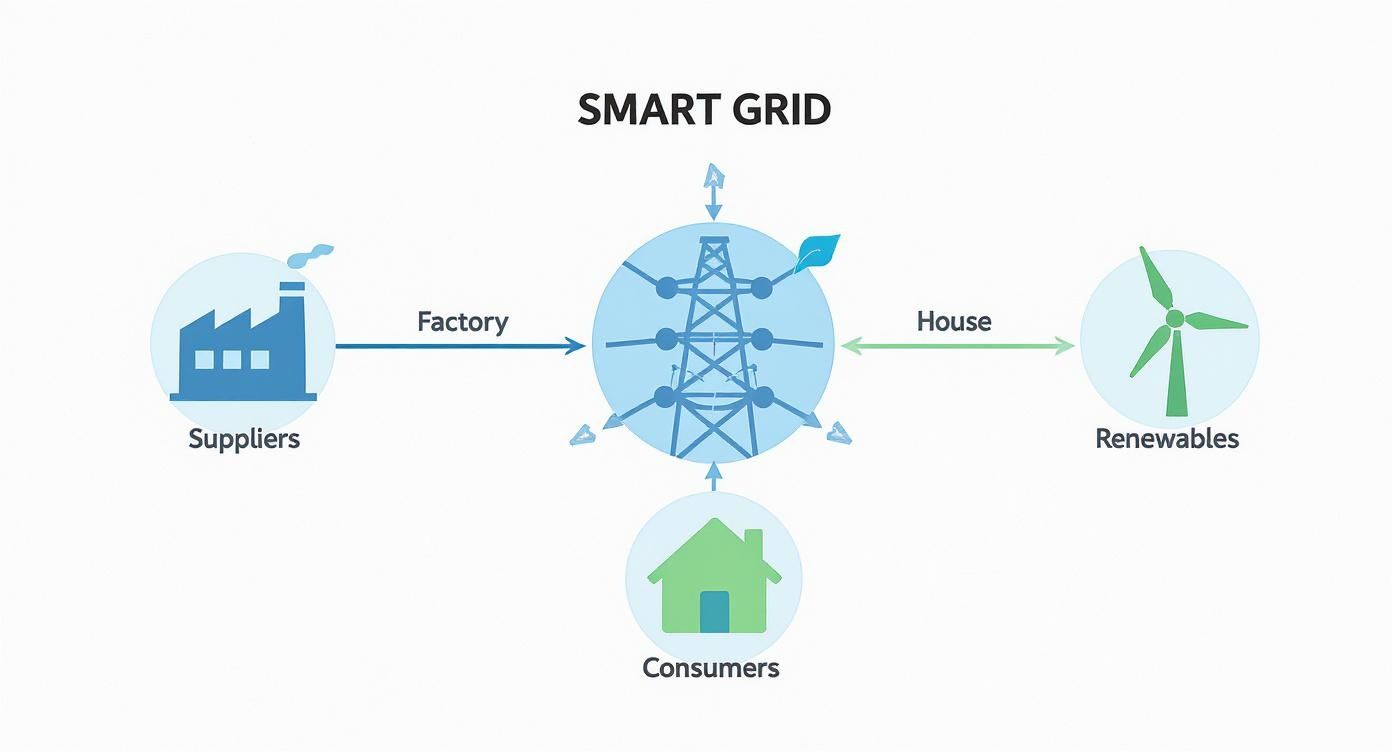 As you can see, smart grid solutions create a connected ecosystem where energy and information flow seamlessly between everyone involved.
As you can see, smart grid solutions create a connected ecosystem where energy and information flow seamlessly between everyone involved.
Distributed Energy and Battery Storage
Another core part of the smart grid is how it handles Distributed Energy Resources (DERs) . These are just smaller-scale power generation and storage systems, like solar panels on a warehouse roof or an on-site battery at a logistics depot. Unlike huge, centralised power stations, DERs create a more decentralised and resilient energy network across the UK.
Of course, you cannot just have power coming from thousands of different places without some coordination. Smart grid solutions are essential to orchestrate these scattered resources. Without intelligent management, injecting power from countless small sources could easily destabilise the grid. A smart grid, however, can coordinate them all, using local solar generation to power local needs or storing excess wind energy in nearby batteries for later.
This brings us to a crucial technology: grid scale batteries . These systems function like giant energy reservoirs. They absorb electricity when supply is high and demand is low—say, on a windy night—and then release it back into the grid during peak hours to keep everything stable.
This ability to store and release energy on demand is a real game-changer for several reasons:
- Renewable Integration: It smooths out the stop-start nature of wind and solar power, helping create a more reliable supply.
- Grid Stability: Batteries can respond in milliseconds to fluctuations, preventing blackouts before they happen.
- Constrained Connections: They allow for high-power activities like rapid EV charging even where the grid connection is weak, acting as a local power buffer.
This commitment to upgrading our grid is backed by serious investment. The UK smart grid market, currently valued at USD 2,417.4 million , is projected to rocket to USD 8,835.9 million by 2033. That’s a growth rate of 15.49% every year, supported by major initiatives like National Grid ESO's £58 billion investment plan. Together, these technologies are creating a flexible, robust and intelligent network that's ready for whatever the future holds.
Powering the UK's EV Revolution
The electric vehicle revolution is well underway but it brings a serious challenge for our national grid. As more and more EVs hit UK roads, the demand for power skyrockets. Just imagine an entire street plugging in their cars after work – the strain on local infrastructure would be immense.
This is where smart grid solutions come in. Instead of digging up roads for hugely expensive grid upgrades, we can use technology to turn this challenge into a powerful asset for managing energy and keeping the grid stable. It’s a far more elegant approach, especially when you consider that a single rapid EV charger can draw as much power as a small block of flats.

Smart Charging and Grid Balancing
At its heart, a smart grid enables smart charging. It’s a simple but profound shift. Instead of your car drawing maximum power the second you plug it in, a smart system talks to the grid to find the best time to charge.
This might mean automatically shifting the charging session to the middle of the night when electricity is cheaper and there’s plenty of renewable energy, like wind power, available. For the driver, it means lower bills. For the grid operator, it means a more balanced and efficient network without the need for disruptive reinforcement works.
Smart grid solutions transform EVs from a passive drain on the network into active participants in a balanced energy ecosystem. This two-way communication allows vehicles to charge when it is best for the grid, not just when it is most convenient for the driver.
This intelligent management is vital for all charging types, but it's particularly critical for high-power needs. A mobile EV charging unit, for example, can be a lifesaver in high-demand areas, but its power draw needs to be carefully managed. A smart system ensures it works in harmony with the local grid, not against it.
Enabling Charging from Constrained Connections
One of the biggest roadblocks to rolling out more chargers is the state of our existing infrastructure. Many perfect locations for chargers—think retail parks or older office buildings—suffer from EV charging from constrained grid connections . They simply do not have the electrical capacity to support multiple rapid chargers.
This is where smart grid solutions, especially when paired with on-site batteries, really shine. A grid scale battery can be slowly trickle-charged from a weak grid connection during quiet periods. When an EV plugs in, that stored energy is unleashed at high speed, delivering a rapid charge without ever tripping the local breaker.
This combination of EV charging and batteries unlocks countless new sites for charging infrastructure. It's a game-changer that removes a major barrier to public charging and ensures the EV transition doesn’t get stuck in the slow lane.
The table below really brings home the differences between the old way and the smart way of doing things.
Smart Charging vs Traditional EV Charging
| Feature | Traditional Charging | Smart Charging |
|---|---|---|
| Grid Impact | High potential for peak load stress and local overloads. | Actively balances grid demand by shifting charging to off-peak hours. |
| Energy Source | Draws power whenever plugged in, often during peak fossil fuel usage. | Prioritises charging when renewable energy is abundant and cheap. |
| Cost to Consumer | Charging often occurs at peak, more expensive tariff times. | Optimises for off-peak tariffs, leading to significant cost savings. |
| Infrastructure Needs | Often requires expensive and disruptive grid upgrades to support demand. | Reduces the need for grid reinforcement by managing the existing load. |
| Future Capability | Limited to one-way power flow from grid to vehicle. | Enables two-way energy flow with Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology. |
As you can see, smart charging isn't just an improvement; it's a fundamental shift in how we think about energy consumption and grid management.
The Future with Vehicle-to-Grid
The most exciting part of this story is Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology. With V2G, an EV battery doesn't just take power from the grid—it can give it back. A fleet of connected EVs effectively becomes a massive, distributed power plant on wheels.
Picture thousands of commuter cars parked at offices during the day. A smart grid could draw a tiny amount of power from their batteries to help stabilise the grid during the afternoon peak, then top them back up before home time. This turns parked cars into valuable assets that strengthen grid resilience, better integrate renewable energy and even create new income streams for their owners. It's the cornerstone of a truly modern, intelligent energy network.
Unlocking Renewables with Battery Storage
Renewable energy sources like wind and solar are the cornerstones of a greener future but they come with an unavoidable catch. The sun doesn't always shine and the wind doesn't always blow. This intermittency makes them unpredictable, creating a real headache for a traditional grid that’s built for a constant, steady supply of power.
This is where smart grid solutions , paired with battery storage, completely change the game.
Think of it like a sophisticated water management system. A traditional grid is a simple pipe running from a river to a town; if the river runs low, the town goes thirsty. A smart grid, however, adds a massive reservoir into the mix.

Orchestrating Energy with Grid-Scale Batteries
In this analogy, grid scale batteries are the reservoirs. When the sun is shining brightly or the wind is blowing a gale, there's often more energy being generated than the grid needs at that exact moment. Instead of letting this valuable clean energy go to waste, a smart grid intelligently diverts it into these huge battery storage systems.
The smart grid acts as the conductor for this entire operation. It uses real-time data on everything from weather forecasts to consumer demand to decide precisely when to store energy and when to release it back.
When evening comes and solar generation drops—just as people get home and switch on their appliances—the smart grid seamlessly calls upon the stored energy from the batteries. This ensures a smooth and reliable power supply and this constant balancing act is absolutely critical for maintaining grid stability.
A smart grid doesn't just accommodate renewables; it actively orchestrates their output. By pairing intermittent generation with reliable storage, it transforms unpredictable power sources into a dependable, 24/7 energy supply for the nation.
Combining On-Site Renewables and Distributed Energy
This principle doesn't just apply on a national scale. It's also incredibly powerful for individual businesses and local communities through the concept of distributed energy . This simply means a network of smaller, localised energy assets like rooftop solar panels, on-site wind turbines and batteries.
Imagine a logistics depot with a large roof covered in solar panels and a fleet of electric vehicles. This setup creates a powerful microgrid with combined on-site renewables, EV charging and batteries .
- During the day: The solar panels generate electricity. This power can run the facility and provide EV charging for the fleet, with any excess stored in an on-site battery.
- During the night: When the sun goes down but the depot still needs power, it draws from the energy stored in its battery. If the EV fleet needs a top-up, the battery provides the power for rapid EV charging without straining the main grid.
- During grid outages: The entire site can disconnect from the main grid and run independently on its stored solar power, ensuring complete operational resilience.
This combination of on-site renewables, EV charging and battery storage is a perfect example of smart grid solutions working at a local level. It gives businesses greater energy independence, significantly cuts electricity bills and reduces their carbon footprint.
By managing their own energy, they also help to relieve pressure on the wider grid. Better yet, these local systems can even support the national network. A smart grid can communicate with thousands of these distributed energy sites, asking them to release stored power back into the grid during times of extreme demand. This turns countless small producers into a coordinated, virtual power plant.
The ability of a smart grid to manage this complex, multi-directional flow of energy is fundamental to our energy future. You can learn more about how grid-scale battery storage is powering the UK and its vital role in building a more robust, flexible and sustainable energy system for everyone.
Real-World Benefits of the UK's Smart Grid
It’s one thing to talk about the theory behind smart grid solutions but the real-world impact is what truly matters for the UK. When we move these concepts out of the lab and into our communities, we see tangible improvements in reliability, cost-efficiency and our environmental footprint.
One of the most immediate effects is a far more resilient power network. Think of a smart grid as a self-healing system. It uses an array of sensors and automated controls to spot faults the moment they happen. Instead of a single fallen power line causing a massive blackout, the grid can instantly isolate the problem and reroute electricity, often restoring power to most homes and businesses in seconds.
Driving Down Costs and Empowering Consumers
For households and businesses across the UK, the biggest draw is often the potential for serious cost savings. Smart grids make this possible through clever energy management. They enable demand-side response programmes , which actually reward people for shifting their electricity use away from peak times. This isn’t just about saving a few quid; it’s about everyone actively helping to balance the entire network.
And this isn’t some far-off future concept—it's happening right now. The push for greater energy efficiency and better integration of renewables is accelerating smart grid adoption in the UK. By the end of 2023, a staggering 33.9 million smart meters were already installed in UK homes and small businesses.
People are getting involved. During the winter of 2023/24, 2.6 million households and businesses signed up for the Demand Flexibility Service, collectively saving 3.7 GWh of electricity . If you want to dive deeper into this shift, you can read the full details on UK grid reform to grasp the true scale of the change.
This intelligent management means we do not have to fire up expensive, polluting power plants just to handle short bursts of high demand. The outcome? A more stable grid and lower energy bills for everyone.
Fostering a Greener, More Sustainable Future
Beyond the financial perks, the environmental benefits are massive. Smart grid technology is the key to unlocking the full potential of renewable energy and slashing our carbon emissions. When the wind is blowing and the sun is shining, the grid can prioritise that clean power or store the excess in large-scale batteries for later.
This drastically cuts our dependency on fossil fuels and plugs the leaks of wasted energy across the network. By optimising everything—from charging our EVs overnight to running heavy industry during off-peak hours—the entire system operates with a level of efficiency we’ve never seen before.
A smart grid doesn't just manage electricity; it actively manages our carbon footprint. By making renewable energy more dependable and reducing waste, it provides the backbone for the UK's net-zero ambitions.
As smart grids become woven into the fabric of our cities, we also have to think about the bigger picture. This technological leap forward means we need to get serious about responsibly managing e-waste in smart cities to ensure our progress is sustainable from start to finish. Smarter energy use, seamless renewable integration and responsible technology management—that’s the real impact of this national upgrade.
Navigating the UK's Smart Grid Rollout
Upgrading an entire nation's energy infrastructure is a monumental task and the UK’s journey toward a fully functional smart grid is no exception. It’s a project that goes far beyond just installing new technology. We’re talking about coordinating millions of individual installations, earning public trust and building a secure digital backbone for our country's energy future.
A core piece of this puzzle is the smart meter. These devices, installed in homes and small businesses, are the eyes and ears of the smart grid, feeding it the real-time data it needs to work intelligently. The programme has made huge strides but there’s still a way to go.
The Smart Meter Rollout Progress
Millions of properties across the UK are now connected to the smart meter network. As of early 2025, that figure stood at around 20.5 million UK homes and small businesses.
But the progress hasn't quite kept pace with initial targets. The government’s 2025 goal isn’t met yet, with just under two-thirds ( 64% ) of all eligible properties having a smart meter by the close of 2024. You can dig into more of these smart meter statistics at Uswitch.com.
Getting a meter into every property is a huge logistical challenge but the work continues. Alongside the physical installations, a massive effort is underway to make sure the whole system is tough enough to handle modern digital threats.
Addressing Cybersecurity and Future Challenges
Connecting our national grid to the internet opens up incredible possibilities but it also creates new vulnerabilities. A huge part of the smart grid puzzle is protecting this critical infrastructure from cyberattacks. This means building multiple layers of security to defend everything from the individual meter in your home to the central systems managing the network.
The goal is to build a grid that is not only intelligent but also inherently resilient. This means creating a system that can pre-empt, withstand and rapidly recover from both physical disruptions and digital attacks, ensuring a secure energy supply for decades to come.
Tackling these hurdles is a central part of the rollout plan. It involves continuous investment in secure tech, public awareness campaigns to build consumer confidence and tight collaboration between the government, regulators and industry partners. This clear-eyed view of the challenges ahead shows just how committed the UK is to getting this right and building a cleaner, more secure energy network.
Your Questions Answered
Here, we tackle some of the most common questions we hear about smart grid solutions in the UK. Let's clear up the practical details and show you how this technology works in the real world.
Are Smart Meters Compulsory in the UK?
No, you do not have to get a smart meter. While energy suppliers are required by the government to offer one to every home and small business, you have the right to say no.
That said, these meters are a cornerstone of the wider smart grid. They feed back the real-time data needed to run an intelligent, responsive network. For you, the benefits are clear: no more manual meter readings and a detailed picture of your energy use, which is the first step to managing your bills more effectively.
How Do Smart Grids Help with EV Charging from a Weak Grid Connection?
This is where smart grid solutions really shine, especially when dealing with a weak or constrained grid connection. They use intelligent load balancing that constantly monitors the local grid's capacity. Think of it as a traffic controller for electricity, ensuring power is distributed efficiently without causing a jam.
If the grid starts to feel the strain, a smart charging system can automatically dial down the charging speed for a short while. It might even shift the charging session to off-peak hours when there's plenty of power to go around. This is a key benefit for EV charging from constrained grid connections .
This simple, automated adjustment prevents local infrastructure from being overloaded. More importantly, it often means you can avoid the costly and disruptive process of upgrading the grid itself, making rapid EV charging possible in far more locations.
What Is Demand-Side Response and How Does It Work?
Demand-side response, or DSR, is a clever programme that pays energy users to scale back temporarily their electricity consumption when the entire network is hitting a peak. It’s a collective effort to keep the grid balanced.
Here’s how it works in a nutshell:
- Grid Signal: The network operator sees a spike in demand coming and sends out a signal asking for a temporary reduction in energy use.
- Consumer Action: Businesses and individuals enrolled in a DSR scheme can then choose to power down. An industrial site might pause non-essential machinery or a smart EV charger could automatically hit pause on a charging session.
- Incentive: For that flexibility, participants are rewarded, usually with a payment or a credit on their energy bill.
It's a smart way to balance supply and demand without having to fire up extra power stations, leading to a cleaner, more efficient and more affordable grid for everyone.
Ready to build a smarter, more resilient energy future for your business? ZPN Energy provides market-leading rapid EV charging, battery storage and integrated smart grid solutions. Discover our technology today at https://www.zpnenergy.com.








